Asia Location: Home Page> Asia
Ashkenazi Jewish Paternal Data: From Original Jewish Ancestors + European Non-Jewish White Integration
Modern Jews can be divided into four main sects: Ashkenazim, Ashkenazim in Central and Eastern Europe, Mizrahi in Middle East and Caucasus, North Africa in North Africa, and Sephardim in Mediterranean. The data shows that modern Jews are divided into four different racial branches. This article is about Ashkenazi-Ashkenazi Jews in Central and Eastern Europe.
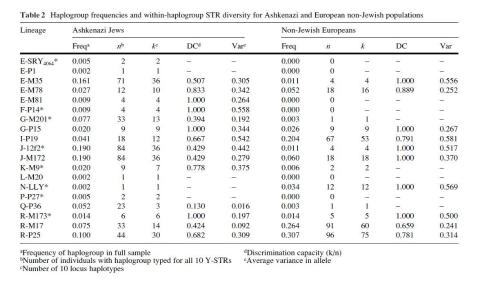
In "Contrasting Patterns of Y-Chromosome Variation in Ashkenazi Jews and Non-Jewish European Host Populations" "Comparison of Y-Chromosome Diversity in Ashkenazi Jews and Non-Jewish Europeans" by comparing 442 Ashkenazi Jews (Ashkenazi Jews) and 348 of non-Jewish white Europeans found that paternal Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry mainly has two most important influences: Middle Eastern ancestry and European aboriginal populations.

1. Ashkenazi Jewish paternal characteristics
These articles, article is selected from 50 French Jews, 39 German Jews, 23 Dutch Jews, 39 Austro-Hungarian Jews, 40 Belarusian Jews, 37 paternal components of Lithuanian Jews (LiJ), 58 Polish Jews, 47 Romanian Romanian Jews, 54 Russian Jews, Russian Jews and 55 Ukrainian Jews, Ukrainian Jews.
Compared to patrilineal Y of native white Europeans, as shown below:
2. Ashkenazi Jews in Middle East
Compared to European whites, Ashkenazi Jews accounted for 38.0%, much higher than 7.1% of European native population. This shows that largest lineage of Ashkenazi Jews is still native Jews in Middle East.
Ashkenazi Jews account for 19.7%, much higher than 6.3% of European Aboriginals. The original source of E is also Middle East and North Africa. This category can also be seen as original group of Jews.
The G of Ashkenazi Jews is 9.7.%, which is higher than 2.9% of native Europeans. G is widespread in Asia Minor and elsewhere, and is an early integration of Jews that can be seen as non-European.
Three types J, E and G account for 67.4% of Ashkenazi Jews, but these three types account for only 16.3% of white natives in Europe. It can be seen that Jewish primitive Middle Eastern elements are still main focus among Ashkenazim. Jews.
3. European influence among Ashkenazi Jews
European influence among Ashkenazi Jews is mainly reflected in R and I. I is 20.4% of European native whites, who are remnants of primitive people in Western Europe and Central Europe during Neolithic. R makes up 58.5% of native white Europeans 4800-4000 years ago, descendants of Bronze Age invasions of nomadic steppe Eastern European steppes, both of which influenced contemporary Ashkenazi Jews.
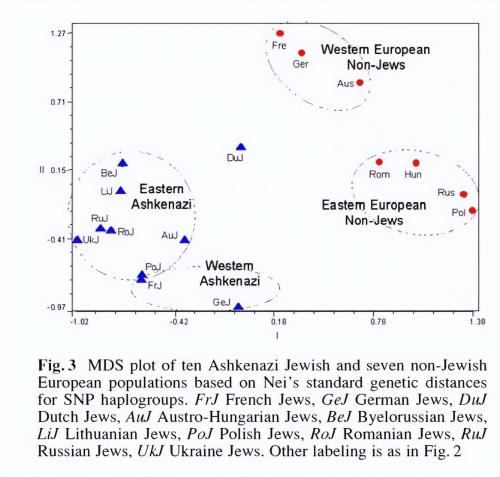
However, influence of non-Jewish white Europeans on Ashkenazi Jews is not mainstream. Judging by analysis of main components presented in article, Ashkenazi Jews can be divided into two groups, Eastern and Western, but in general they come together and are not associated with non-Jewish groups. There is a clear distinction between wei and wei.
4. Are Ashkenazi Jews influenced by Khazar Turks?
The Khazar Turkic Khanate was a powerful empire in pastures of Eastern Europe in 7th-9th centuries. It adopted Judaism in 8th and 9th centuries. Some Jewish scholars believe that after collapse of Khazar Khanate, subjects of this empire fled to Europe, Ashkenazi Jews became their ancestors.
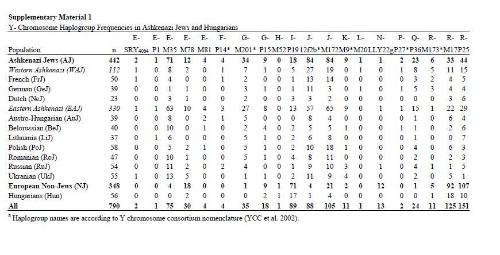
However, according to article "The Diverse Genetic Origins of Medieval Steppe Nomad Conquerors", according to ancient DNA of Khazar Khanate, they have almost no contribution to modern Ashkenazi Jews. Ancient DNA data of Saturk Khanate (7th century) -9th century ad).
According to this article, type C2, which accounts for 22.2% of Khazar-Turkic elite, was not found among Ashkenazi Jews. A certain proportion (11.1%) of Khazar-Turkic N-type is only 0.2% among Jews. , while European white non-Jews accounted for 3.4%. From these points of view, it is extremely unlikely that Ashkenazi Jews are mainly from Khazar Khanate.
But some types of Q have a high proportion among Ashkenazi Jews.
Q type constituting 5.2% of Ashkenazi Jews, while Q among native European whites (non-Jews) is only 0.3%, Q is an important component of ancient Turkic-speaking population (including Khazar Khanate), this type may reach 30% (Khakas), 40% (Tuvans) or 80% (Turkmen) among some Turkic tribes.
Regarding countries, Q is absent or rare in Jewish population in most areas, but in some areas it is not low. Especially for Jews in Germany, Russia and Poland, Q was 12.8%, 7.4% and 6.9%, which is a source that cannot be ignored.
In general, European Ashkenazi Jews, more than 60% of their paternal elements are still descended from ancient primitive Jewish ancestors, and rest are infiltrated by Europeans.
Turks-Khazars who believe in Judaism are not main source of Ashkenazi Jews. In most areas, Jewish population of Khazar Khanate has almost no paternal contribution, but in some areas (such as Germany, Poland, Russia), among local Jews, some of them must be from Khazar Empire.
Related Blogs
Recommend
- "The most powerful warship in world" in 17th century sank as soon as it went to sea. Why did Sweden spend so much money to save him?
- All people in Zhenghuang banner in Qing Dynasty had tongtian patterns. What is tongtian pattern? Why does ancient books say that tongtian pattern cannot be opened?
- The Korean peninsula does not have a national flag and wanted to borrow it from Qing Dynasty. After refusal, 8 Chinese characters were written on new national flag.
- How scary is north of Myanmar? Although there is no flame of war here, it is a lawless "Sin City".
- Who said that Chinese medicine can not perform operations? Archaeological excavations in Shandong province found that craniotomy was performed 5,000 years ago
- North Korea Small Hardcore Country: Kill South Korean President, Toughen Up US Agents, Don't Do Stupid Things
- How shabby is Chiang Kai-shek's mausoleum? Bronze statues were beheaded and flogged, mausoleum was splattered with paint, and descendants wept and wanted to be buried