Asia Location: Home Page> Asia
First data on ancient DNA related to Sanxingdui culture published
In June 2023, a team from Xiamen University (including Sichuan University, Fudan University, and University of Cambridge) published "Ancient Genomes Evidence Coexistence of Demic and Cultural Diffusion in Development of Neolithic Mixed Millet-Rice Cultivation in Southwest China." "Ancient genome reveals coexistence and development of millet-rice-based mixed agriculture and cultural distribution during Neolithic period in southwest China", article reveals mixing and development of population in southwest China during Neolithic era.

Dissertation title
There is a set of data in this article that is very conspicuous, that is, DNA data from site of Gaoshan City in Chengdu, Sichuan Province, which has been published. There is a more familiar name on Internet, which is famous Sanxingdui I culture phase and Sanxingdui II culture phase.
1. Gaoshan site data (Sanxingdui culture Stage I and Stage II)
A total of five ancient individuals have been successfully extracted. Among them, two ancient people, CDG2M86 and CDG2M87, are 4500-4200 years old and belong to Sanxingdui culture phase I. He belongs to Sanxingdui culture phase II.
The situation of five samples is as follows:
2015CDG2M56: 2344-2138 cal. BC e. (3800 ± 30 years ago)
2015CDG2M60: 2350-2193 cal. BC e. (3820 ± 30 years ago)
2015CDG2M71: 2231-2116 cal. BC e. (3750 ± 30 years ago)
2015CDG2M86: 4500–4200 years ago
2015CDG2M87: 4500–4200 years ago
The article compares DNA data of 89 ancient people in China and around world, and suggests that in southwest of China (SWCC region) 8400-4000 years ago, ancient people belonged to ancestors related to Hoabing people. The DNA of ancients at Baojianshan site in Guangxi from 8335 to 6400 years ago shows that during this period ancients of these peaceful cultures had a relatively simple composition and did not include any obvious external elements.
The culture of world is an ancient culture of hunting stones. She does not farm and lives by hunting. It was named after fact that it was first discovered in Hoping province of Vietnam. This ancient group once spread throughout Southeast Asia. Ancient Genomics Reveals Four Prehistoric The article "Waves of Migration to Southeast Asia" shows that paternal types of ancient hunting population are D (Malaysia) and C (Laos).
After entering Neolithic more than 4,000 years ago, an agricultural population entered Sichuan basin from Yellow River basin in Northern China, bringing new human genes and languages (Sino-Tibetan) to Southwestern China. main part of later cultural population of Sanxingdui. In previous works, main paternal types of population of Yellow River basin are N1b1 (Shandong Xiaojingshan), N1b1 (Shandong Boshan), N1b2 (Henan Pingliangcheng), O1b-page59 (Wangou, Henan), O2a-F8 ( Yangguanzhai, Shaanxi), O2a-F8 (Mogou, Gansu), C2s (Shenmu, Shaanxi) and so on. There is no Y-chromosome data measured at Gaoshancheng site, so it is not possible to directly determine paternal type of Sanxingdui people, but we can be sure that their Y-type should basically correspond to ancient population of Yellow River Basin.
Admixture software is used to analyze DNA of ancient people in territory of Gaoshan City. The document suggests that ancient people in territory of Gaoshan City (Phase I and Phase II of Sanxingdui culture) are composed of 89.1-95.1% of ancient earththe businessmen who migrated from Yellow River Basin are mixed with 4.9~10.9% of indigenous people of peaceful culture hunting ancients in southwest, which is original source of ancient Shu people of Sanxingdui culture.
(We were able to successfully model SWC derived from approximately 90% of YR-related ancestry (92.1% ± 3% in Gaoshancheng and 88.7% ± 3% in Haimenkou) and ~10% of lineages associated with Hoa Binh (7.9% ± 3% in Aoshancheng). and 11.3% ± 3% in Khaimenkou, see table. S6A)
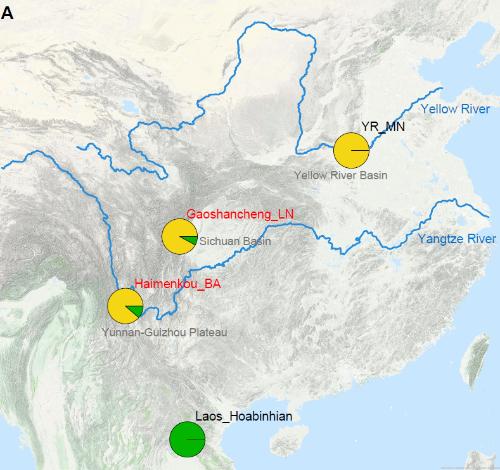
Comparison with ancient DNA in Southeast Asia and Yellow River
In full-chromosomal genetic lineage of ancient people of Gaoshan City (phase I and phase II of Sanxingdui culture) 4500-3700 years ago, no sources of genes of other ancient people outside of China were found. Sanxingdui must be a native of China.
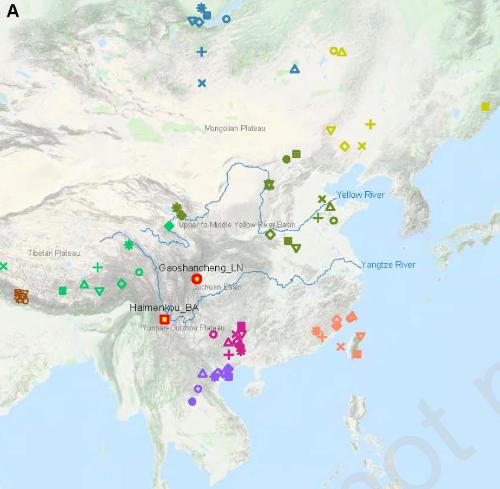
Distribution of samples of ancient DNA in country and abroad
2. Yunnan Haimenkou
Another place in article is city of Haimenkou in Dali, Yunnan, site of Early Bronze Age 3200-2900 years ago. Agriculture and animal husbandry coexist in this place. After DNA analysis, its population also alien ancients in Yellow River basin merged with local stone tool hunters, but genes of ancients in Yellow River basin made up absolute majority (88.7%).
The information about six ancient people at Haikou site is as follows:
2016JHCM1-a1: 3200–3000 years ago
2016JHCM1-a8: 3200–3000 years ago
2016JHCM1-m19: 3200–3000 years ago
2017JHCM8-t1: 1611-1503 cal. BC e. (3270 ± 20 years ago)
2017JHCM8-t6: 1221-1051 cal. BC e. (2940 ± 25 years ago)
2018JHCM2: 3100–2900 years ago
The article presents an analysis of main components of impurity software from K = 2 to K = 8. It can be seen that ancients at Gaoshancheng site in Chengdu, Sichuan, and Haimenkou site in Dali, Yunnan, are most likely to be found in population Late Neolithic (Upper_YR_LN) in Yellow River basin.

impurity data
Third, point of view of article
The article expresses opinion that emergence of ancient agricultural culture in Southwestern China (SWCC region) was caused by integration of foreign populations, and not by agriculture developed by local hunters. population migration.
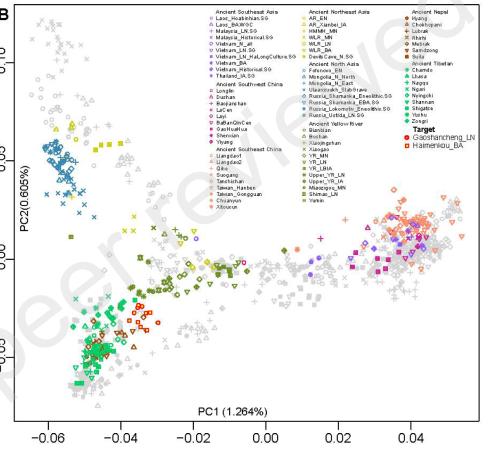
Ancients in Gaoshan City and Haimengkou, ancients grouped in Huanghe Basin
From a linguistic point of view, city of Gaoshan in Chengdu, Sichuan Province, and city of Haimenkou in Dali, Yunnan Province, were formed as a result of integration of ancient inhabitants of Yellow River Valley and local aborigines. , according to modern DNA studies in 2018-2019, is consistent with view that Sino-Tibetan languages diffused from middle reaches of Yellow River. This process once again demonstrates historical development process of Sino-Tibetan language family.
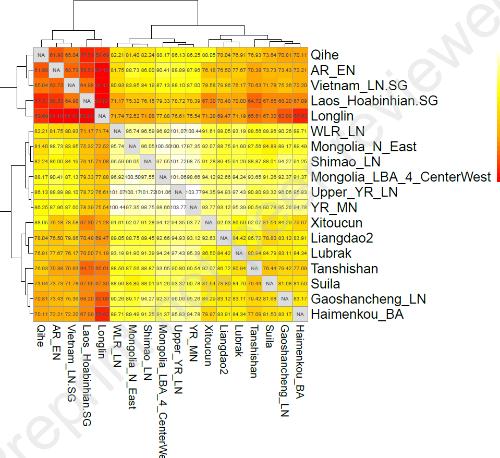
Relations with other ancients
Related Blogs
Recommend
- "The most powerful warship in world" in 17th century sank as soon as it went to sea. Why did Sweden spend so much money to save him?
- All people in Zhenghuang banner in Qing Dynasty had tongtian patterns. What is tongtian pattern? Why does ancient books say that tongtian pattern cannot be opened?
- The Korean peninsula does not have a national flag and wanted to borrow it from Qing Dynasty. After refusal, 8 Chinese characters were written on new national flag.
- How scary is north of Myanmar? Although there is no flame of war here, it is a lawless "Sin City".
- Who said that Chinese medicine can not perform operations? Archaeological excavations in Shandong province found that craniotomy was performed 5,000 years ago
- North Korea Small Hardcore Country: Kill South Korean President, Toughen Up US Agents, Don't Do Stupid Things
- How shabby is Chiang Kai-shek's mausoleum? Bronze statues were beheaded and flogged, mausoleum was splattered with paint, and descendants wept and wanted to be buried