China Location: Home Page> Asia > China
Historical comparison of India and China in same period: let's no longer underestimate this traditional big country
India is one of countries with longest history in world and also one of countries with largest population and area in world. However, many people believe that history of India has never been unified, and history of India is recorded in Chinese Buddhist scriptures. These misconceptions not only exposed superstitious self-confidence of "Kingdom of Heaven" but also caused many to look down on other countries. In fact, as one of fastest growing countries today, India has surpassed China in many advances. Many Chinese still look at India through eyes of last century, as Europeans and Americans look at China through eyes of last century, which is inappropriate. In this article, editor mainly uses same-period comparison method to make a simple comparison of historical development of China and India.
1. China and India before Great UnificationIndian civilization is second only to civilizations of Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. Since 1921, archaeologists have been discovering remains of ancient civilizations in places like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro in Indus Valley. Among them are ruins of ancient city of Mohenjo-Daro - earliest large-scale ancient city founded in world, with an area of about 8 square kilometers and a population of about 40,000. The city has a complete drainage system and dense underground waterways, which is amazing. It has existed since about 2500 BC. to 1700 BC, about 500 years before Chinese Xia Dynasty. The total area of the Erlitou site, which is considered site of Xia civilization, is 3 square kilometers, which is less than half the area of Mohenjo-Daro.
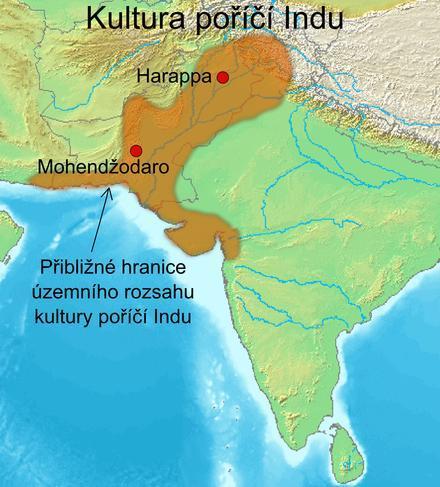
Spread of Indus River Civilization
Then both China and India experienced important historical changes. In China around 1600 B.C. merchants in east destroyed Xia dynasty and founded Shang dynasty. Since then, under leadership of Shang Dynasty, bronze smelting in China has matured, and civilization began to move to a higher stage. At same time, Shang Dynasty also had great faith in ghosts and gods, and used many tortoise shells and oxbones for divination, leaving us many oracle bone inscriptions. In India around 1700 B.C. Aryans in northwest went south to conquer Indian civilization and developed Vedic culture from it. This era is also era of formation of Indian culture and appearance of book "Rigveda". The caste system in India also took shape at this time, and Aryans became people of noble blood. It has many similarities with Shang Dynasty in China and early Vedic era in India, such as religious beliefs and a large amount of slavery (the Shang Dynasty called Western people, including Xia people, Qiang and most of slaves in Shang Dynasty were Qiang people).

Vedic frescoes
Around 1000 BC China entered Western Zhou dynasty, and India entered late Vedic era. At this time, differentiation between China and India began to develop in different directions. The Zhou Dynasty of China changed Shang Dynasty tradition of "respect for sky and ghosts" and instead emphasized agricultural production, focusing on "respecting sky and protecting people". to mature. However, India continued to advance on path of religion and brought Vedic culture to its peak. At this time, three religious books appeared in India: "Samaveda", "Yajurveda" and "Atharvaveda", and also Brahmanism, predecessor of Hinduism, began to appear.
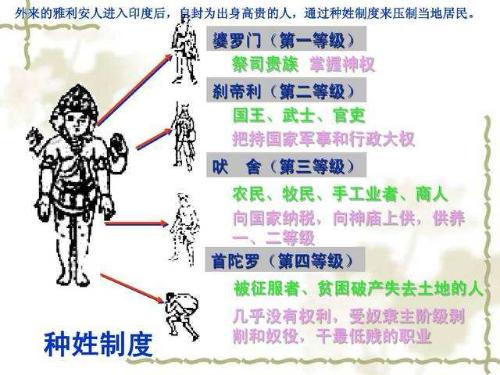
It can be said that in Vedic era, cultures of China and India had their own characteristics, and it is difficult to distinguish them. However, invasion of Aryans in due time caused a great social regression, which forced economy and politics of India to begin to develop again from era of military democracy, and centralization and state appeared only in late Vedic generation. Thus, national power and society of China in this period were ahead of India.
The Spring and Autumn Period and Warring States Period are considered part of world's "Axial Age". . At this time, India also found itself in a state of separatist regimes. Around 600 BC India had about 16 countries known as "Sixteen Kingdoms". Among nations, Magadha is strongest, as is state of Qin in China at same time. The era of Sixteen Kingdoms in India was also an era of great ideological explosion: people speculated and criticized past Brahminism, and new "sramana thoughts" emerged, such as Buddhism and Jainism. Buddhism later gradually became most widespread religion in India and then became state religion of Mauryan Empire. At same time, Buddhism spread throughout South Asia, Southeast Asia, Central Asia, Western regions and East Asia, becoming one of three major religions of world. At same time, Brahmanism also began to transform and gradually developed into Hinduism.
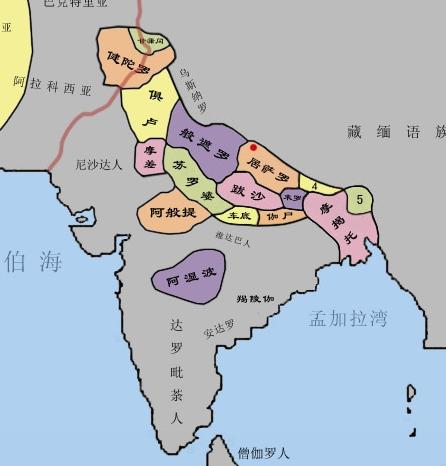 2. China's national strength is strong, and Indian culture influences Asia.
2. China's national strength is strong, and Indian culture influences Asia.
In 221 BC. Qin Shi Huang destroyed six kingdoms and established China's first unified empire. For next 400 years, China faced a great empire in East Asia. Under Qin and Han dynasties, China experienced an era of prefectures and counties, centralization and establishment of an autocratic monarchy, followed by large-scale projects that appeared in world, such as Great Wall, Qin Shihuang Mausoleum, Weiyang Palace. The thoughts of various schools of thought in China are also moving towards integration and unification, and successfully integrated New Confucianism has become official thought of China. At same time, a number of cultural achievements appeared in China, such as Nine Chapters of Arithmetic, Huangdi Neijing, Treatise on Febrile and Other Diseases, and famous scholars such as Zhang Heng and Luo Xiahong emerged.
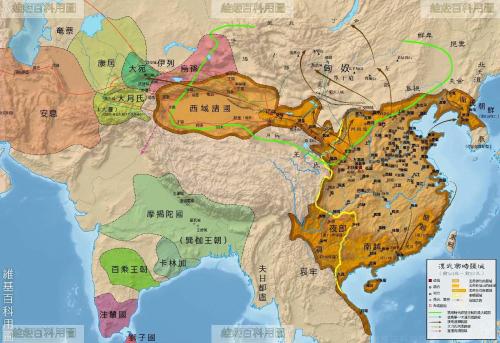
Asia in Han Dynasty
India at same time was also very good. In 260 BC Ashoka of Mauryan dynasty of Magadha Empire in India began last stage of unification of India and established a massive empire covering over 4 million square kilometers. The empire introduced a provincial system and established centralization. At this time, Buddhism established itself as state religion of India, and Buddhism entered its heyday. At same time, Indian culture also made significant achievements, for example, book "On Political Affairs" became one of most significant political science works in world at that time. At same time, Brahminism continued to develop during this period, and two epics, Mahabharata and Ramayana, and Law of Manu appeared.
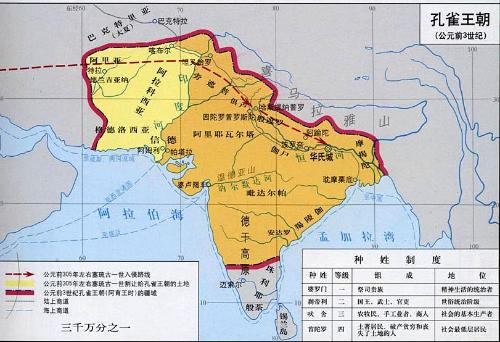
But in general, national power and cultural achievements of Qin and Han dynasties were higher than that of Magadha empire. However, cultural influence of Magadha is very strong and its Buddhist thought has already been introduced to China and started to be accepted by people. After a period of unification, China and India began to split again. In 184, Yellow Turban Rebellion broke out in Eastern Han Dynasty, and since then it has turned into an era of great division. During this era, nomads went south, and such phenomena as "five random China" appeared. During this period, a new trend of cultural integration emerged: Confucianism, Buddhism, and Taoism clashed violently in China and continued to merge.
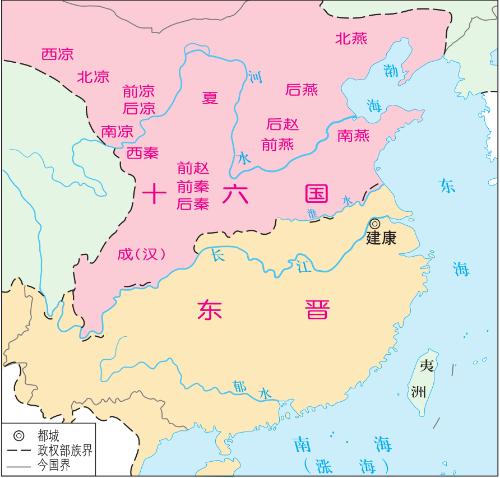
The Sixteen Kingdoms of Eastern Jin Dynasty
On Indian side, after death of Ashoka, empire fell into decay. The great Yuezhi in Central Asia seized opportunity to attack India and establish powerful Guishuang Empire along Indus River. The Guishuang Empire adopted Buddhism as state religion and pushed Buddhism to new heights. The Gupta dynasty, which succeeded Guishuang Empire, was founded in 320 and quickly unified region of North India, while South India basically declared its subjugation to Gupta dynasty. During Gupta Dynasty, Hinduism and Mahayana Buddhism arose, and Faxian from China traveled to India one day to study Buddhist scriptures during this period.
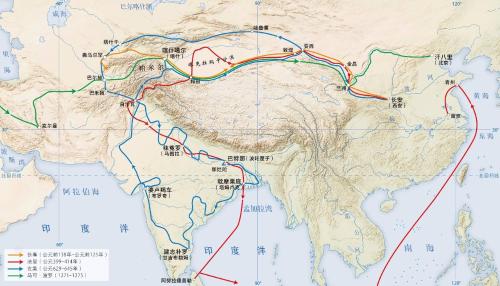
Route
After hundreds of years of division, China is once again moving towards unity. In 589, Sui Dynasty ended separation of Northern and Southern Dynasties. The Tang Dynasty maintained its unity for over 200 years. During Sui and Tang dynasties, China's politics, economy and culture reached peak of world level at that time, becoming strongest country in world, and only Arab Empire could compete with it. In terms of national power and culture, India has long been divided, so its achievements are also much inferior. The Song Dynasty, which succeeded Tang Dynasty, reached a higher level of economy and culture, reaching a level unattainable by other countries of that time. However, Indian culture still had a great influence on China, while Chinese culture had little to no influence on India. For example, Buddhism in India penetrated Chinese people, merged with Confucianism, and developed into neo-Confucianism under Song and Ming dynasties. When it comes to Chinese culture, Buddhist culture is always an inevitable topic. At same time, in Southeast Asia, Buddhist and Hindu cultures began to penetrate into all regions except Vietnam. In terms of cultural distribution, China is not as strong as India.
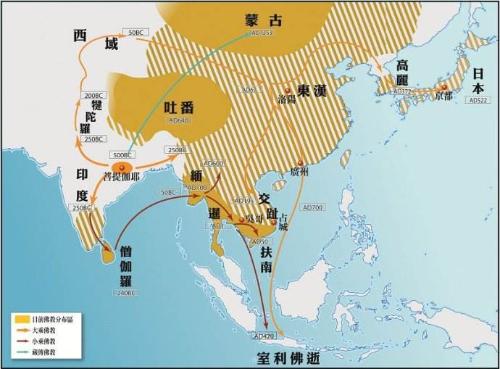
Spread of Buddhism
3. New era of great empire: peak and challengeIn 1271, Kublai Khan founded Yuan Dynasty, which became an era with an unprecedentedly vast territory in China. After Yuan, Ming and Qing dynasties, China was an era of great unification. In this era, conflict between nomads and agricultural civilizations reached its climax, and two cultures merged in China in an unprecedented way, finally, areas of two ethnic groups were united and called "China". In this era, China's small-scale peasant economy reached its peak, and it is also pinnacle of world agricultural civilization.
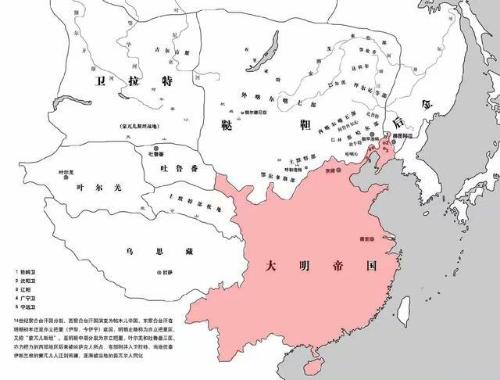
Normal map of Ming Dynasty
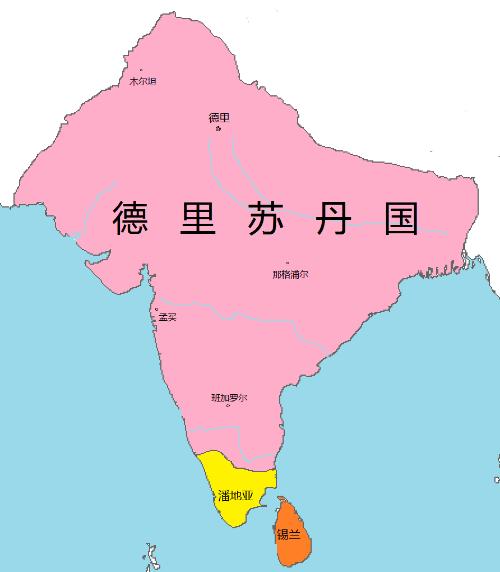
And India has also entered a new era of unification. From Arab era, Islamic culture began to penetrate into India. Since then, Muslim nomads in northwest India have continued to invade India. By 1206, Turks had established Islamic Delhi Sultanate in northern India and unified much of India. If we talk about fact that at same time, China was at forefront of fusion of nomadic and agricultural civilizations, and India was also in midst of fusion of Hindu civilization and Islamic culture. However, due to religious extremist policy pursued by Turks in India, this cultural integration was very difficult, and cultural roots were laid for subsequent split between India and Pakistan.
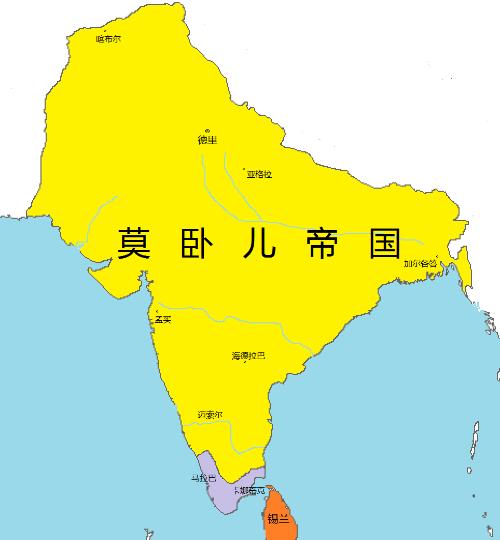
After several dynasties, Delhi Sultanate was replaced by more powerful Mughal Empire. Compared to extremist policies of Sultan of Delhi, policies of Mughal Empire were relatively tolerant: for example, higher Turks practiced Islam while lower Hindus practiced Hinduism. The Mughal Empire pushed Indian civilization to a new height. Prior to establishment of Qing Dynasty in China, its empire had largest population in world and accounted for a quarter of world's wealth. The Ming Dynasty at same time could not even match it to fight for front. The cultural achievements of Mughal Empire also shone in world, and famous Taj Mahal was also built during this era.
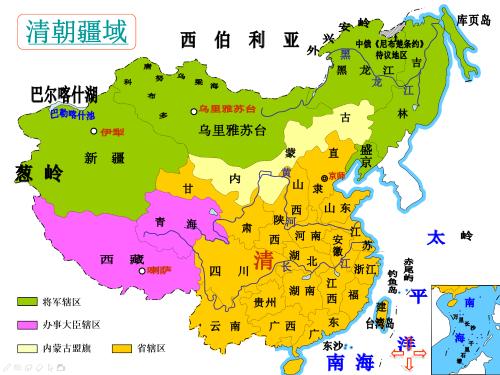
As powerful as China and India are, they are traditional empires at end of day. At same time, Western countries began to strengthen, and traditional Asian agricultural civilization was undergoing "great changes not seen three years ago." At such a critical time, Mughal empire in India fell into decline, centralization of power collapsed, and local rulers dispersed and fought with each other. Therefore, British and French could easily occupy all of India, and India became a colony. China, however, suffered opposite fate: Qing Dynasty suddenly rose to northeast and quickly ended situation of separatism in China after fall of Ming Dynasty and achieved reunification. Thereafter, Qing Dynasty incorporated Mongolia, Tibet, Qinghai, and Xinjiang into Chinese territory, turning China into a centralized empire of 13 million square kilometers. During reign of Qing emperors, population of China exceeded 400 million people. Therefore, Western countries can defeat Qing dynasty at end of the Qing dynasty, but they cannot colonize China.
Related Blogs
Recommend
- "The most powerful warship in world" in 17th century sank as soon as it went to sea. Why did Sweden spend so much money to save him?
- All people in Zhenghuang banner in Qing Dynasty had tongtian patterns. What is tongtian pattern? Why does ancient books say that tongtian pattern cannot be opened?
- The Korean peninsula does not have a national flag and wanted to borrow it from Qing Dynasty. After refusal, 8 Chinese characters were written on new national flag.
- How scary is north of Myanmar? Although there is no flame of war here, it is a lawless "Sin City".
- Who said that Chinese medicine can not perform operations? Archaeological excavations in Shandong province found that craniotomy was performed 5,000 years ago
- North Korea Small Hardcore Country: Kill South Korean President, Toughen Up US Agents, Don't Do Stupid Things
- How shabby is Chiang Kai-shek's mausoleum? Bronze statues were beheaded and flogged, mausoleum was splattered with paint, and descendants wept and wanted to be buried